Hey Coders! In this article, I'm gonna break down how the internet actually works. It's incredible how a video we are watching on our phones traveled thousands of miles from a Google Data Center to reach us. Let's learn how the internet works by getting to understand the details of this data's incredible journey.

The data centers which can be thousands of miles away from us have the videos, images, and data stored inside them. So you ask, how does this data reach into mobile phones or a laptop? It can be achieved by Satellite, from the data centers a signal could be sent to the satellite via an antenna, and by another antenna the signals reach our phones. But due to the long distance of travel, it causes significant delay in the process and causes huge latency.
If not Satellite then what? Well, it is done with the help of optical cables which connect between the data center and our devices. Our Phone can be connected to cellular data or wifi but at some point, it is connected to this network of optical fiber cables.
So where is data stored and how?
The data is stored in a solid-state device within the data center. This SSD acts as the internal memory of a server. The server is simply a powerful computer whose job is to provide the video or other stored content when we request it. Now the challenge is how to transfer the data stored in the data center specifically to the device via the cables.
Every device that is connected to the internet is identified uniquely by a string of numbers known as IP address. It's just like our home address, any mail or letter sent to us reaches us precisely because of the address. The IP address also acts similarly as a shipping address through which all information reaches its destination. The Internet service provider allots the IP address of our device.
The server in the data center also has an IP address. The server stores a website so we can access any website just by knowing the server's IP address. However, it is difficult for a person to remember so many IP addresses, so to solve this problem domain names like facebook.com, youtube.com, etc are used which corresponds to IP addresses. The server has the capability of storing several websites and if the server consists of multiple websites all the websites cannot be accessed with the server's IP address. In such cases, additional info, host headers are used to uniquely identify the website.
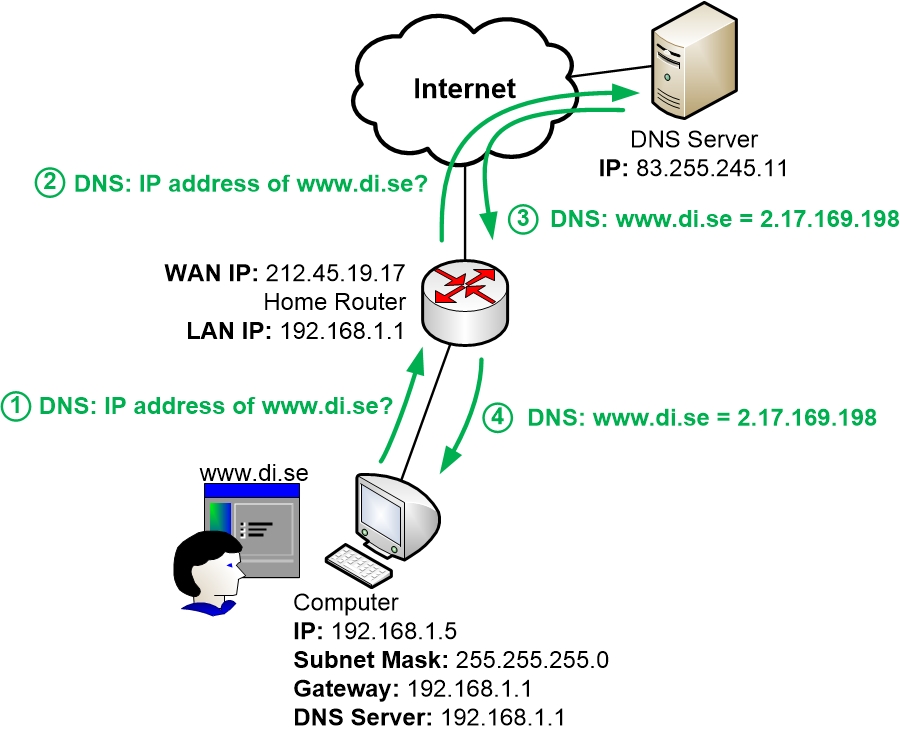
To access the internet we always use domain names instead of complex IP address numbers. From where does the internet get IP addresses corresponding to our domain name requests. For this internet uses DNS(Domain Name System). When we search for something, the browser sends requests to the DNS server to get the corresponding IP address. After getting the IP address, the browser forwards the requests to the data center, once the server gets the request to access a particular website the data flow starts. The data is transferred in digital format via optical fiber cables ( optical cable companies- AT&T, Orange, Verizon, Google) to the router which then converts the light signals to electrical signals. Then an ethernet cable is used to transmit the electrical signals to your laptop. However if we are accessing the internet using cellular data from the optical cable the signal has to be sent to a cell tower and from the cell tower, the signal reaches your cell phone in the form of electromagnetic waves.
All the data that the Data Center sends to us is in the form of a huge collection of 0s and 1s known as packets and transmitted. Let's assume these streams of zeros and one are divided into different packets by the server where each packet consists of 6 bits. Along with the bits of the data, each packet also consists of the sequence number and the IP address of the server and your phone. With this info, the packets are routed towards the device.
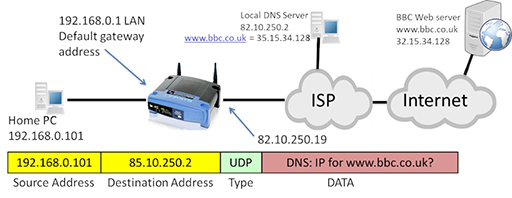
Upon reaching the device the packets are reassembled according to their sequence number. If it is the case that any packet fails to reach the device and acknowledge is sent from the device to resend the lost packets. Internet uses Protocols for the management of the flow of data packets.
I hope this article has given you a basic idea about how the internet works. Thank you for reading till the end. Happy Coding!

